This article is from our Febooti archive, it was relevant then, and I think that it is still relevant today.
If you remember the computers of an earlier day then you surely remember the old MS-DOS. If you are of the more recent generation of computer users then you have also probably seen, used or at least heard of MS-DOS. If you are not one of the aforementioned, MS-DOS is an acronym for Microsoft Disc Operating System. This is just yet another Microsoft operating system.
However, unlike the Microsoft operating systems, you are probably used to, Microsoft Windows 95, XP, Windows 7 or Windows 8, for example, you won’t see any neat little graphics to which you are able to click. These newer operating systems are often times called Graphical User Interfaces, or GUI. MS-DOS does not care about anything called an icon, wallpaper or screen saver. Rather than being considered as a Graphical User Interface MS-DOS is what is known as a command-line interface (CLI). You type commands on what is called the command line.
When using a command-line operating system, you enter commands to accomplish tasks. Once you have worked with this type of system you would soon realize that there are many command combinations that you enter frequently. This is where the use of batch files becomes ingenious in that when you want the computer to perform a given combination of commands an abundant number of times, a batch file can store the details of that command combination for swift execution.
Therefore a batch file is a sequence of commands you would typically enter in a command prompt. Batch files are often used to start programs and run utilities. This is because batch files can allow these events to happen with fewer commands. Automation is possible as well to further the advantages of batch. Batch files accomplish all of this while remaining relatively small in file size.
Now, how does this relate to Batch scripts? Once you make a script (program), it will run in this screen. Not exactly. We won’t run our scripts in the actual MS-DOS, more of a watered down readily accessible version Windows provides us. The command prompt – this is where you will see any output produced. This screen, among being called a command prompt, is often referred to as simply a DOS prompt, command line or a MS-DOS prompt.
You are also able to open and modify programs from the command prompt. When writing batch scripts you will soon become quite familiar with this screen. Since most of us are using Windows XP, 7 or 8 that will be the primary operating system for which the examples herein will be for. However when worthy, references will be made towards previous versions of Windows. So, to actually run the batch scripts we make we need to be able to access the command prompt.
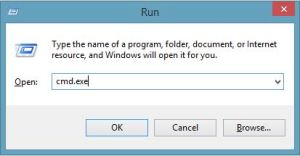
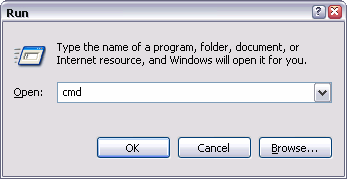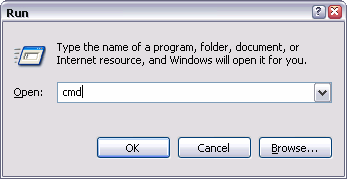
How to get MS-DOS prompt? To access the command prompt you simply click the Start button in the lower left hand corner of the screen followed by clicking on the Run… option. On newer Windows 8 and 8.1, just press Windows key on the keyboard, and type CMD.exe
When you do this, a small box will appear in the lower left hand corner of the screen. To access the command prompt simply type cmd (Windows XP, Vista, 7).
The command prompt is similar to MS-DOS. The command prompt is a great tool that has many great uses. One way of harnessing those uses in one file and not having to type the command for that use each time is through a batch file.
Next article tomorrow.
This article is from our Febooti archive, it was relevant then, and I think that it is still relevant today.
Edit Oct 17, 2014: added link to the next article.