Photo: freeimages.com
This article is from our Febooti archive, it was relevant then, and I think that it is still relevant today (a few details changed).
Previous article: What is a batch script?
Next article: Stopping a DOS batch file
Now we are familiar with the command prompt. Batch scripts are one or more DOS commands that are executed sequentially, and the script is written using a text editor. This does not mean you can use Microsoft Word or Google Docs or any other of those fancy programs you might use to type up a report. Those types of programs are called word processors, not text editors. Besides the obvious that these programs allow you to change colors and import graphics, these programs add extra formatting that you don’t see.
A great example of a text editor is Notepad. Notepad comes bundled up with Microsoft operating systems (or better choice is open source editor – Notepad++ which supports syntax highlighting). To access Notepad simply click the Start button followed by the Programs option. Next, click on Accessories which is usually at the top of the column. The next pop-up column should contain the Notepad program option. Or on newer Windows, hit Start, and type Notepad.
A helpful hint is to make a shortcut to the Notepad in your desktop or Taskbar by right-clicking on the Notepad option (or Pin to Taskbar on the newer Windows). Subsequently select Send To followed by selecting Desktop (Create a Shortcut). This allows quick access in the future by placing an icon on your desktop. A shortcut can also be made using batch.
At this point I highly recommend to download the Notepad++, or change Folder options in the Windows, to see file extensions, so you can easily change .txt file extension to the .bat for the batch files.
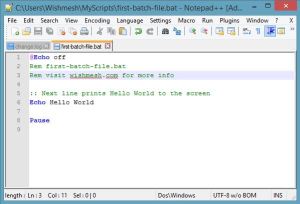
Now that we have the Notepad open we can begin scripting. Let’s begin by printing the words Hello World to the screen. Type the following into Notepad screen. Then save our new text file as helloworld.bat or my-first-batch-script.bat, or anything you like.
@Echo off
Rem helloworld.bat
:: Next line prints Hello World to the screen
Echo Hello World
Pause
Now let’s explain what each line does.
The computer has a habit of taking everything you type and storing it verbatim. This can be annoying and troublesome at first however you will soon realize that predictability is nice. Anyway, this means that all commands will be seen by the end-user. This makes for a very ugly and bothersome execution.
To circumvent this we will type @ECHO OFF at the first line. ECHO OFF makes sure that command echoing is turned off. This fixes our previous problem. However, it creates a new one. ECHO OFF is a command thus it will also be seen. That is where the use the @ (at) sign comes in. This stops the echo of the ECHO OFF command. If you were to leave the @ sign out you would see ECHO OFF above your Hello World message as part of your output.
The majority of the batch scripts have this snippet of code at the beginning. You can also turn echoing back on if you like by using the command ECHO ON. If you type ECHO by itself the status of ECHO will be displayed. The ECHO OFF command only turns off command echoing. The output from the DOS commands will still be seen.
When you copy a file in a batch file, you will still see the 1 File(s) copied message. If you use a batch file to start a GUI program, that program will indeed appear on the screen (For example, Calculator, Notepad, MS Word, MS Excel). ECHO OFF turns off batch file commands seen in the console while that specific batch file is running.
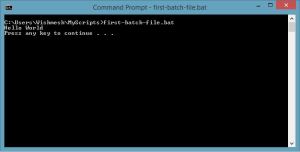
Here is a screenshot of your first batch file’s output:
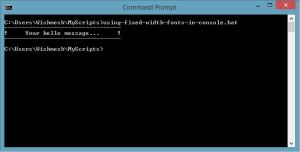
The ECHO command is great for communicating with the user. Messages and questions can be easily delivered to the end-user. This is great for giving the user a list of choices and wanting feedback before a particular action is performed. Try experimenting with different formats for delivering messages to the user. For example, centering the text using spaces (this works because most consoles uses fixed-width fonts by default). Or adding hyphens and exclamation marks for borders:
@echo off
echo ---------------------------------
echo ! Your hello message... !
echo ---------------------------------
You can create a line break, a blank line, by typing ECHO. but notice the period mark after the echo command. The ECHO and period combination is what creates the line break. Example:
@ECHO OFF
REM helloworld.bat
:: Prints 'Hello World' to the screen...
:: with a line break in between the words.
ECHO Hello
ECHO.
ECHO World
PAUSE
Lines 2, 3 and 4 in this batch file example are comments or remark statements. When writing batch scripts you will want to place two comments at the top of the file. Coding standard style should be in place, which improves the quality of software which results in fewer bugs which is easier to maintain and use. The first line should contain the name of the file and the second remark statement should include a brief statement about the following program. This helps yourself when you start writing many batch files and it also helps someone else (for example, your colleagues) read your script that might not be as familiar with it as you. This could perhaps be the case of having a friend debug your file.
The first remark statement has the REM signifying a remark. Such remarks are used in every programming language to add comments to your code. Since your first batch scripts will be smaller programs, we won’t need very many remark statements, though it is a good idea to get in the habit of documenting your scripts well. Remark statements are ignored by DOS. Notice the :: (two colons) in the next remark statement. This is another way of commenting your batch scripts. The double colon approach is a better way of commenting your code because the command prompt will entirely ignore this line making your program run faster.
Yes, REM is ignored however the command prompt takes a more detailed approach at reading the comment and it takes a longer amount of time to execute (not relevant on modern PC). The double colon makes for a quicker program. This gives you advantages when you start building more complicated programs and you start adding more of them. For the preceding reasons we will not use the REM command rather we will use the double colons when commenting our code.
Another characteristic of batch scripting is that line breaks (spaces between lines) in your batch file are ignored. Here they are used merely for readability. Notice the two above / previous examples each have a different line break scheme. The first implements a double space layout for better readability. The second is more compact.
ECHO is similar to the PRINT command in other programming languages. ECHO is used for displaying a string of text to the screen.
Finally, we have the PAUSE command. Your program will run just fine without this. However, you will not be able to see your output; the text Hello World in this example. If you include the PAUSE command you will see the text string Press any key to continue… If you do not include this command the command prompt may appear, then flash away quickly (depends on how you run batch scripts). Run the program without this and note the difference (first run by double clicking mouse, second – from the CMD.exe console).
Note that batch commands are usually not case sensitive. All caps are shown in this article to help you identify the batch code. When an instance arises where case-sensitivity will matter it will be explained.
This article is from our Febooti archive, it was relevant then, and I think that it is still relevant today (a few details changed).
Edit Oct 9, 2014: Updated formatting and added link to the next article.